innovation-matters.info
A community for innovators
Ecosystems Defined
Ecosystems defined in the context of Innovation
The concept of ecosystems has long been applied in science to understand biodiversity, the relationships between organisms and their environment, and the sustainability of ecological systems. In business, ecosystems are concerned with collaborations, value creation, innovation, and adaptability within interconnected networks. Ecosystems are essential for digital innovation as they provide access to diverse expertise, foster collaboration and partnership opportunities, offer access to funding and resources, facilitate validation and market insights, and enable growth opportunities and synergies for innovations. By actively participating in ecosystems, digital innovators can leverage the collective power of collaboration and accelerate their journey towards successful digital innovation. Distinguishing between product ecosystems, entrepreneurial ecosystems, and innovation ecosystems is crucial for understanding the different purposes, characteristics and dynamics in each context.
The table below provides selected definitions for each concept from credible sources. While the definitions differ in some respects, they also share several characteristics. For example, there is agreement that entrepreneurial ecosystems focus on the supportive environment that enables the growth and success of start-ups and entrepreneurs, like Fishburners in Sydney Australia (see Table below). Innovation ecosystems encompass the collective network of organizations, institutions, and individuals that foster innovation and drive technological advancements to address a specific shared concern, like the advancement of quantum technology (see Table below). Product ecosystems concern the range and complementarity of products around a core technology, such as hearing solutions (see Table below).
Table: Ecosystems defined
Innovation Ecosystems
Entrepreneurial Ecosystems
Product Ecosystems
Definitions
"Innovation ecosystems are loosely structured but highly dynamic networks of organizations, individuals, and resources that collectively contribute to the innovation process, enhancing creativity, and accelerating the development and diffusion of new technologies and solutions." Reference: "Innovation Ecosystems: A Critical Examination," MIT Sloan School of Management (2019).
"Entrepreneurial ecosystems refer to the social, economic, and cultural factors that influence an area's capacity to promote and support entrepreneurship." Reference: "Entrepreneurship Ecosystem Project," Babson College (2014).
"A product ecosystem is the network of products and services that surround a core product, enhancing its functionality and creating a more comprehensive solution for the user." Reference: Gartner Glossary.
"Innovation ecosystems are collaborative networks of stakeholders that encompass governments, businesses, academia, and civil society, which aim to create an environment conducive to innovation, economic growth, and societal development."Reference: "Fostering Innovation-Driven Entrepreneurship in Europe: A Framework," World Economic Forum (2014).
"Entrepreneurial ecosystems are the networks of organizations, individuals, and resources that facilitate the development and growth of entrepreneurship within a region, creating a supportive environment for startups and small businesses." Reference: "Entrepreneurial Ecosystems Around the Globe and Company Growth Dynamics," World Economic Forum (2014).
"Product ecosystems are comprised of diverse components that collaborate to provide a holistic and user-centric experience. These components can include hardware, software, services, and even partnerships."Reference: "The 8 Principles of Product Ecosystems," IDEO (2018).
"Innovation ecosystems refer to networks of companies and other institutions that join forces to create innovative products and services, from start-ups to multinational corporations." Reference: "The Age of Continuous Connection: Innovation Ecosystems and the Impact of Digital Technologies," Harvard Business Review (2017).
"Entrepreneurial ecosystems are dynamic networks of organizations, institutions, and individuals that work together to create an environment that fosters entrepreneurship and innovation." Reference: "How to Build an Entrepreneurial Ecosystem," Harvard Business Review (2018).
"A product ecosystem encompasses a set of complementary products, technologies, and services that work together to fulfil customer needs. These components create an integrated and cohesive user experience." Reference: "The Age of Continuous Connection: Innovation Ecosystems and the Impact of Digital Technologies," Harvard Business Review (2017).
Examples
Australian researchers and organizations have made notable contributions to the field of quantum computing. Australia has made significant progress in increasing the public profile of quantum technology, with CQC2T (Centre of Excellence for Quantum Computation and Communication Technology) Director UNSW Professor Michelle Simmons named as Australian of the Year for 2018.
Sydney is one of Australia's major entrepreneurial hubs, with a concentration of start-ups, co-working spaces, and venture capital firms. Organizations like the Sydney Start-up Hub and Fishburners provide support and resources to start-ups.
Cochlear, an Australian company, has developed a range of hearing implant solutions and related services. Their products create an ecosystem around hearing technology, improving the quality of life for individuals with hearing impairment.
© Innovation Matters 2022
The figure below illustrates the linkages between ecosystems. For example, innovation ecosystems can be a catalyst for entrepreneurial ecosystems. Product innovations are fueled by entrepreneurial ecosystems with new offerings and supported by innovation ecosystems with new discoveries.
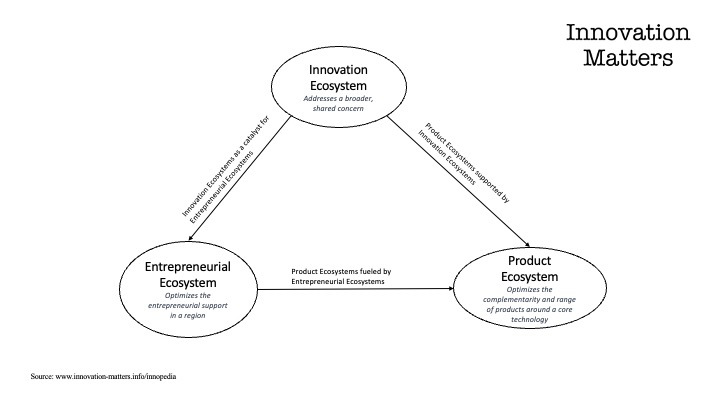
Figure: Linkages between Product Ecosystems, Innovation Ecosystems and Entrepreneurial Ecosystems